Nonwovens In Textile Industry And It's Applications
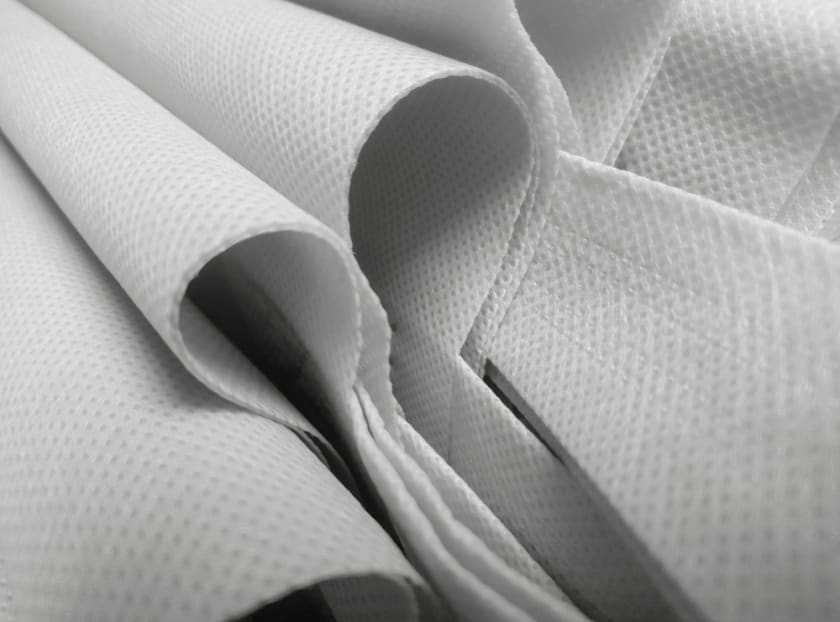



Nonwoven geotextile fabric is made from two or more kinds of fabrics, bonded together through solvent treatment, heat, or chemicals. Unlike other fabrics such as cotton or silk — which are weaved or sewn together — nonwoven geotextile fabrics are made through non-natural treatment to the fabric that strengthens when brought together. The term ‘nonwoven’ is a literal interpretation of the fabric, which denotes the lack of weaving required to make the product.
Nonwoven geotextile fabrics are durable, disposable and are often marketed as one-time-use products. They break down easily and more quickly than their woven counterparts and are used as a sustainable and cheap alternative to plastic, cushions, and foam.
Today, nonwoven geotextile fabrics are used in a ton of industries, including apparel, home furnishings, health care, engineering, industrial and consumer goods. Let’s explore the fascinating appeal, and beyond!
Historical Background of Nonwoven Geotextile Fabric
The use of nonwoven geotextile fabrics can be traced to the early 1930s. The outrage over the waste from manufacturing cotton gave birth to the ideas of recycling and repurposing waste, which led to the creation of nonwoven fabrics. Initially, the nonwoven geotextile fabric was made from discarded materials from a cotton mill. The nonwoven textile industry is relatively new, with new avenues of utility cropping up every year. After the Second World War, as nations scrambled to restart their economy with whatever resources they had, the use of nonwoven fabric gained steam in American and European nations. The cost-efficient production of the fabric is one of the biggest reasons behind its spike in popularity.
The first commercial production of nonwoven geotextile fabrics began in the US in the year 1942 by producing fabric from combined fibres. The market for nonwoven products continues to have tremendous potential for growth.
Basic Features of Nonwoven Geotextile Fabric
- The nonwoven fabric consists of one or more layers of fibre.
- Nonwoven geotextile fabrics are porous and flexible.
- The properties of two or more woven fabrics are combined together to serve the purpose of the fabric.
- Nonwoven products are bulky and are used as padding.
- The texture and appearance of the fabric resemble that of plastic.
- All nonwoven geotextile fabrics have multiple uses.
Manufacturing Processes of Nonwoven Geotextile Fabric
There are many popular ways to manufacture nonwoven geotextile fabrics. The most common one is the special binding technique, wherein small fibres are put together on a web or sheet before a machine interlocks them with serrated needles and adhesives. Another process is thermal binding, in which the binder is melted onto the web through heat. Here are some others in practice:
- Melt-blown: The extrusion of melted polymer fibres through a die with 40 holes per inch to form long stretched fibres which are then cooled down with the passage of hot air. The most common use of the melt-blown technique is in the feminine care diaper industry.
- Staple nonwovens: A four-step process to cut and spin the fibres before putting them into bales and then blending them through a uniform web. Staple nonwovens are often used in high-end textile insulations.
- Flashspun: The dispersion of resin in a chamber to evaporate the solvent.
- Wetlaid: Use of solution polymers, emulsions, or other chemicals to bring the pieces of fibre together.
- Air-laid paper: Use of wood pulp to carry and form the structure of paper through the tightening action of the air.
The Properties of Nonwoven Geotextile Fabric
Nonwoven geotextile fabrics are bonded together by filaments or entangled fibre. The use of the thermal, chemical or mechanical processes to bring the fabric together justifies the nomenclature of the product. Although they exhibit similar characteristics as plastic, nonwoven geotextile fabrics have an entirely different set of uses and properties.
Here are the main properties of nonwoven geotextile fabric:
- A nonwoven geotextile fabric has a paper-like feel and resembles the touch of woven fabrics.
- It is soft in touch but has plastic-like durability.
- It is porous and flexible.
- It is often stiff, hard, with pliable.
- It lacks drapability, and can’t be pressed without losing its structure.
- It is often paper-thin.
- It has distinguishable launderability, although the disposal differs from each cloth.
Rising Influence of Nonwoven Geotextile Fabric In the Textile Industry
The industry for nonwoven products is soaring at an astronomical pace, and much can be credited to its environment-friendly and cost-effective production. With the peaking price rise of petro-based raw materials such as polyester, nonwoven fabric has become a default choice for large scale operations.
There’s plenty to be considered in the utility of nonwoven fabric as well. It is softer, recyclable, lighter, and eco-friendly. Many new companies are charting new paths with their use of nonwoven geotextile fabrics, with the latest trends denoting a switch from 100% original textile production to 50% renewable material and heat-free assimilation of the fabric.
The global nonwoven fabrics market is set to grow by approx. USD 12 billion in just five years. The 2020 estimate of the annual global market stands at USD 40.5 billion. The growth is largely credited to the multifaceted application of the fabric in various items of basic utility such as hygiene products, medicine, construction, etc.
Use of Nonwoven Fabric in Apparels
The markets are warming up to the use of nonwoven fabric in the readymade apparel industry. Several sections of the market such as shoes, activewear, SWAT uniforms, bulletproof vests, and luxury clothing have embraced the use of nonwoven fabric in recent years. Moisture absorption, flexibility, and durability are some of the reasons why the fabric has become a go-to in the areas of activewear, coats, shirts, and other everyday clothes. Some of the other properties that make the case of nonwoven textiles a viable apparel fabric are its robustness and lower tensile strength.
Application of Nonwoven Fabric in the Textile Industry

There are many uses for nonwoven products, as markets continue to invest and expand their utility. Nonwoven fabric is used in disposable goods, consumer items, and many other purposes. The reason why the use of nonwoven goods continues to expand is because of its low cost and diversified applications. In industries where single-use products are usually used such as nursing homes, schools and hospitals, nonwoven fabric is the top choice of fabric.
The common applications of nonwoven fabric are:
Disposable items
Nonwoven cloths are engineered to be durable and single-use. Disposable items are generally used as shields or protection that must be discarded after their intended use. Gloves, shoe covers, bath wipes, plasters, and wound dressings are all disposable items that popularly use nonwoven geotextile fabric.
Personal hygiene products
The absorbing property of the fabric play a significant role in the utility of personal hygiene products. Pads, diapers, and napkins required leak-proof absorption enabled by the component-blocking function of nonwoven products.
Medical products
The many properties of nonwoven fabric such as liquid repellence, resilience, and sterility allow for nonwoven products to be used in the field of medicine. Isolation gowns, surgical drapes, surgical gowns, covers, suits, caps, surgical masks, surgical scrubs, medical packaging, and bandages are all made of nonwoven geotextile fabrics.
Consumer durables
Packaging, batting, and lamination are all properties of nonwoven geotextile fabrics, enabled due to its natural porosity. Carpet backing, composites, marine sail laminates, chopped strand mat, backing/stabiliser for machine embroidery, shopping bags, wall panelling, cushions, mattress cores, padding, insulation, acoustic insulation for appliances, wall-panelling, pillows, cushions, mattress cores, automotive components, and upholstery padding are all made of nonwoven fabric.
Geotextiles
The durability, strength, and flame retardancy of nonwoven products qualify them for perfect use as a geotextile in the construction of infrastructure. Nonwoven geotexliles are used in oadway underlayment, soil stabilisation, foundation stabilisation, canals construction, drainage engineering, erosion control, geomembrane protection, and landfill lining.
Furniture
The cushions and foams used in the seats of furniture are made of nonwoven geotextile fabrics to allow for maximum stretch, water resistance, stain resistance, and durability.
Filters
The nonwoven fabric is see-through and separates waters and other liquids from minute granules. Gasoline, oil and air filtration, coffee filters, water filters, tea bags, pharmaceutical industry, mineral processing, bag filters, liquid cartridge, vacuum bags, and allergen membranes are all made of nonwoven geotextile fabric.
Weather-resistant coverings
Nonwoven fabric is as effective as plastic but far more durable in repelling water. Tarps, tents, lumber wrapping, foot coverings, house wrap, cleanroom wipes, and potting material for plants are all examples of nonwoven products.
In conclusion
The apparel industry is embracing change with each passing day, as innovations in the non-traditional spheres of fabric and clothing sprout from every corner — and nonwoven fabrics are leading the chargee. Nonwoven geotextile fabrics are artificially engineered fabrics that are designed to have a limited life. They are single-use and serve many functions such as absorbency, cushioning resilience, softness, strength, and washability. Unlike traditional fabrics, nonwoven materials aren’t converted from fibres to yarn, and they aren’t knitted or woven. A considerate percentage of nonwoven geotextile fabrics are made out of recycled fabrics.
The advent of newer fabrics such as nonwovens is changing the way the industry functions and signals the shift to sustainable products. It is believed that the coming decade will further cement the global dominance of nonwoven geotextile fabrics in the textile industry. Follow the new trends and old ways of the textiles and beyond with Fashinza.



















